A Major Shift in Government Procurement: Locking in Reliability and Affordability
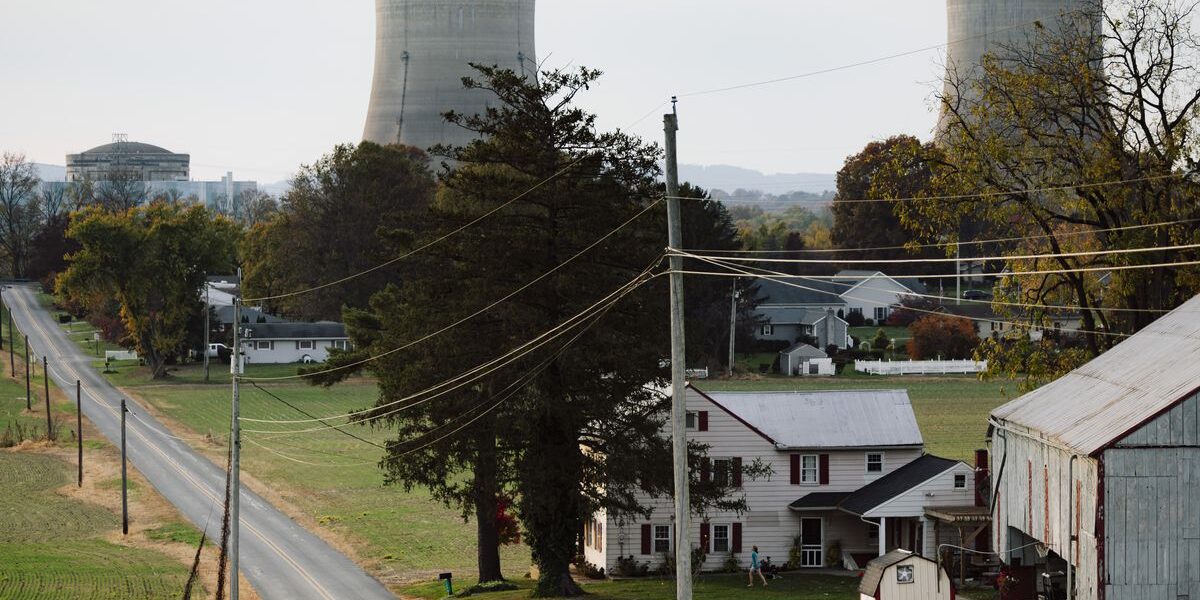
In a significant development, the General Services Administration (GSA) has announced a major nuclear energy contract, marking a turning point in government procurement. This 10-year, $840 million deal is for 10 million megawatt-hours of electricity, equivalent to what’s needed for more than 1 million homes annually.
The Contract Awardee: Constellation
The GSA has awarded the contract to Constellation, which operates the nation’s largest nuclear fleet. This announcement comes on the heels of several big tech companies making a flurry of nuclear energy deals last year.
According to Constellation spokesperson Paul Adams, nuclear energy makes up approximately 4 million megawatt-hours of the deal.
The Significance of Nuclear Energy in the Contract
Silicon Valley is increasingly turning to nuclear energy to satiate electricity demand from AI data centers. The federal government is the nation’s single largest energy consumer, making this contract a big boon to the nuclear industry.
"This agreement is another powerful example of how things have changed," said Joe Dominguez, Constellation president and CEO, in a press release. "Frustratingly… nuclear energy was excluded from many corporate and government sustainable energy procurements. Not anymore. This agreement is another powerful example of how things have changed."
Constellation’s Commitment to Nuclear Energy
Constellation generates 10 percent of the nation’s carbon pollution-free energy, with a majority of its output coming from nuclear energy. The company also produces hydro, wind, and solar power, as well as electricity from gas-fired power plants.
However, Constellation has set a goal of reaching 100 percent carbon-free electricity by 2040, compared to close to 90 percent today.
The GSA’s Vision for the Contract
The contract will allow Constellation to extend licenses for existing nuclear power plants as well as "invest in new equipment and technology" that should result in 135 megawatts of additional capacity. The GSA agreed to purchase 2.4 million megawatt-hours of electricity from this added capacity over 10 years.
The Impact on the Federal Government’s Energy Procurement
This contract is the largest energy procurement contract the GSA has signed in its history, providing budgetary stability and protections from future price increases by keeping electricity costs fixed for 10 years.
"The GSA is framing this contract as a way to lock in more affordable prices as data centers drive up electricity demand and increase competition for limited clean energy sources," says an administration official.
The Role of the Federal Government in Nuclear Energy
Google, Meta, Amazon, and Microsoft have all inked splashy nuclear energy deals over the past year. In September of last year, Microsoft and Constellation announced a plan to restart a shuttered reactor at Three Mile Island in Pennsylvania, the site of the worst nuclear energy accident in US history.
The Biden administration has also made nuclear energy a key part of its plan to transition the US away from fossil fuels to energy sources that don’t cause climate change. Last October, the Department of Energy announced a $1.52 billion loan to help restart a retired nuclear generating station in Covert Township, Michigan.
Nuclear Energy: A Growing Trend in Government and Corporate Procurement
The trend towards nuclear energy is evident in government and corporate procurement. The Trump campaign agenda included efforts to "support nuclear energy production."
This historic contract between the GSA and Constellation demonstrates a growing recognition of the importance of reliable, affordable clean energy.
Key Takeaways
- The General Services Administration (GSA) has announced a major 10-year, $840 million nuclear energy contract.
- The contract is for 10 million megawatt-hours of electricity, equivalent to what’s needed for more than 1 million homes annually.
- Nuclear energy makes up approximately 4 million megawatt-hours of the deal.
- Constellation generates 10 percent of the nation’s carbon pollution-free energy, with a majority coming from nuclear energy.
- The GSA and Constellation have declined to answer questions about how much of the electricity included in the contract will come from each source aside from nuclear power plants.
The GSA is framing this contract as a way to lock in more affordable prices as data centers drive up electricity demand and increase competition for limited clean energy sources.